Robot Arm 3D Scanner
ROS; MoveIt; PCL; Python; C++

This project is a final project for ME495-embedded system class at Northwestern University. The goal of the project is to use an adroit robot arm to hold the object to move and use a fixed RealSense D435 camera to capture the 3D point cloud of this project.
This is the flow chart of the project
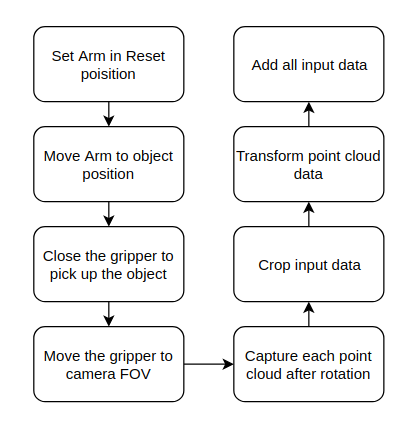
There are two main parts for this project, control of the robot arm and process of the point cloud data. Two different ROS packages deal with these two different aspects.
-
adroit_move
-
realsense_reader
Let’s start from the control of the adroit arm. The arm is HDT Adroit Arm with 6 degree s of Freedoms. Here, I use MoveIt, a widely used software for manipulation to control the robot. The joint of the robot is continuous, which will cause some unexpected behavior for MoveIt path planning, so I set some constraints on the arm joints. Also, the Cartesian path is used for path planning instead of the pure pose goal, which will help the arm to reach the desired pose faster, and accurately. After picking up the object, the arm will lift the object and start rotating, publish finish flag on /arm_state topic after each rotate finish.
Next, let’s talk about the point cloud data processing. After running the realsense_camera and realsense_ros package, the camera will continuously publish the colored pointclouds on the /camera/depth/color/points topic. The cloud data is only dealt with when the arm_state topic received “finish_one” message. Then, I convert the point cloud data from sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 in ROS to pcl::PointXYZRGB, a format used in PCL library for future processing. After that, cloud data is cropped, since we know the transformation from camera depth frame to robot arm end-effector, we can get the position of the center of the object in the camera frame. To caluculate the relative transformation of the two consistent frames, I try to use the transformation from robot arm as a rough estimate and ICP as a finner estimate, however, the ICP couldn’t find enough correspondence, so the calculated transform is the same as the rough estimate. Then , we accumulate the transformation, and transform each point cloud to the coordinate of the first captured frame.
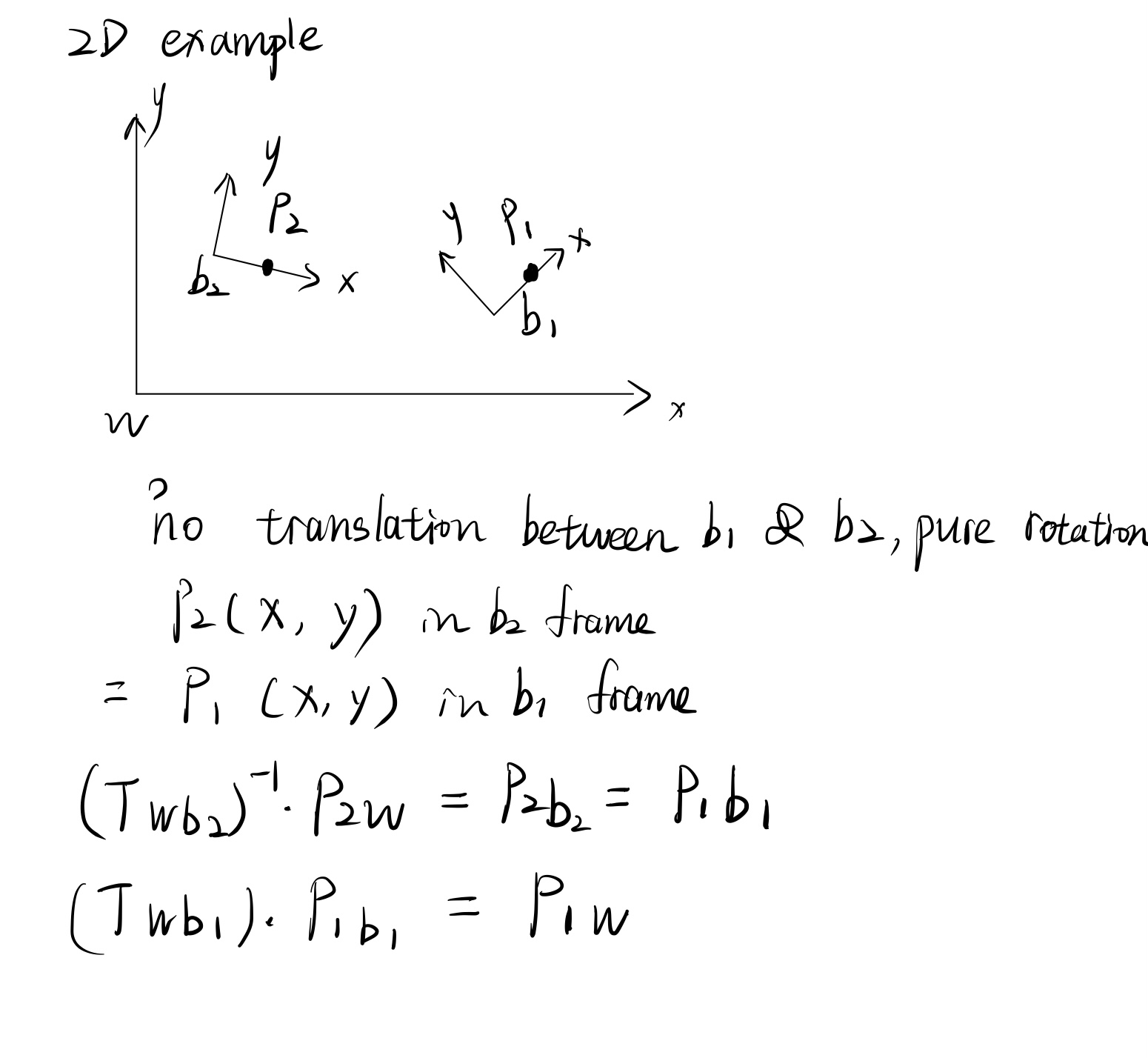
Here is the example for transform the newly accepted point cloud data to the coordinate of the previously accepted point data.
And this is the result after the robot arm reconstruction

This result can be proved by using some method to improve the estimation of pose, like using RTAB-MAP for pose estimation, and use method like teasar for better point cloud reconstruction.
For more details: click here to go to github repository